5. LINES AND ANGLES
5.1.1 INTRODUCTION
[embed]https://vimeo.com/455748601/4ca2d51203[/embed]5.1.2 INTRODUCTION (Notes)
Line:
A line is a straight figure which doesn’t have an endpoint and extends infinitely in opposite directions.
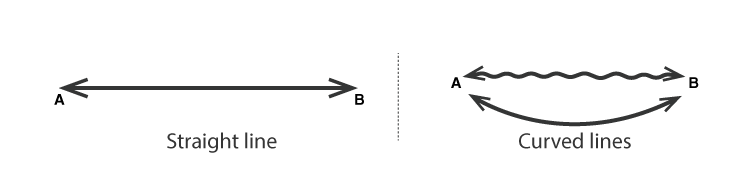
Line Segment
A portion of the line formed with two definite points is called a Line Segment. A line is a one-dimensional figure and has no thickness.
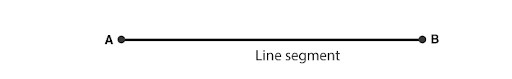
Ray:
A ray is a straight line, which starts from a fixed point and moves in one direction.
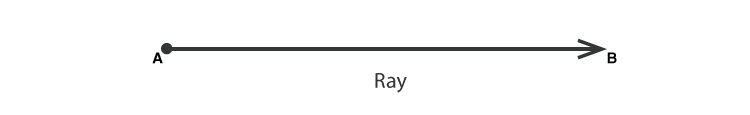
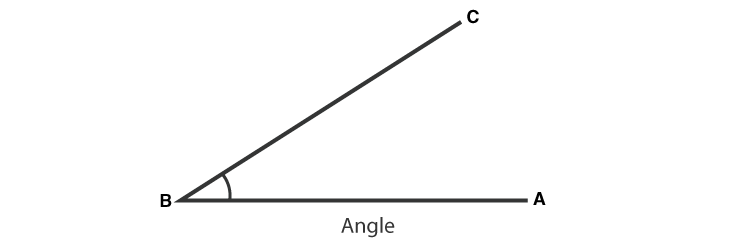
Angle
When we join two line segments at a single point, an angle is formed, or we can say, an Angle is a combination of two line segments at a common endpoint. This common point is called Vertex of the angle and the two line segments are sides or arms of the angle formed.
Types of Angles
There are basically 6 types of angles which are:
| S.No | Types | Defination |
| 1 | Acute Angle | If an angle is less than 90 degrees, then it is called an Acute Angle. |
| 2 | Obtuse Angle | If an angle is more than 90 degrees, then it is called Obtuse Angle. |
| 3 | Right Angle | If an angle is exactly at 90 degrees, then it is called Right Angle. |
| 4 | Straight Angle | If an angle is exactly 180 degrees, then it is called Straight Angle. |
| 5 | Reflex Angle | If the angle is more than 180 degree but less than 270 degrees, it is denoted as a Reflex Angle. |
| 6 | Full Angle | A 360-degree angle is called a Full Angle. |

5.2.1 RELATED ANGLES
[embed]https://vimeo.com/455748646/8a9ccdd470[/embed]5.2.2 RELATED ANGLES (Notes)
Angles
- An angle is formed when two rays originate from the same end point.
- The rays making an angle are called the arms of the angle.
- The end point is called the vertex of the angle.
Related Angles
The different angles are:
| S.NO | TYPES | DEFINATION | FIGURE |
| 1 | Complementary Angle | The sum of the measures of two angles is 90°. | 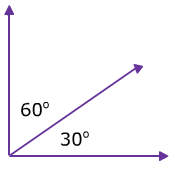 |
| 2 | Supplementary Angle | The sum of the measures of two angles is 180°. | 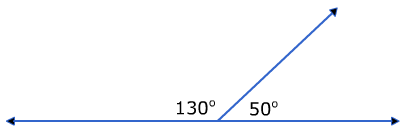 |
| 3 | Adjacent Angle | Adjacent angles have a common vertex and a common arm but no common interior points. |  |
| 4 | Linear pair | A linear pair is a pair of adjacent angles whose non-common sides are opposite rays. |  |
| 5 | Vertically Opposite Angles | when two lines intersect, the vertically opposite angles so formed are equal. |  |
5.3.1 PAIRS OF LINES
[embed]https://vimeo.com/455748760/d27a6fb5f4[/embed]5.3.2 PAIRS OF LINES (Notes)
Pairs of Lines
Intersecting lines:
- Two lines intersect if they have a point in common.
- This common point O is their point of intersection.
Transversal: A line that intersects two or more lines at distinct points is called a transversal.
Angles made by the transversal: There are different angles formed when the transversal cuts the lines. They are:
- Interior angles
- Exterior angles
- Pairs of Alternate interior angles
- Pairs of Alternate exterior angles
- Pairs of Corresponding angles
- Pairs of Consecutive Interior angles.
- Pairs of Consecutive Exterior angles.
Transversal of Parallel Lines: We know that the parallel lines are the lines that do not meet anywhere. Transversals of parallel lines give rise to quite interesting results.
5.4.1 CHECKING FOR PARALLEL LINES
[embed]https://vimeo.com/455748821/74a4f4a2a7[/embed]5.4.2 CHECKING FOR PARALLEL LINES (Notes)
Checking for Parallel Lines
If a transversal cuts two lines, such that,
- If each Pair of Corresponding Angles are Equal in measure.
- If each pair of the Alternate interior Angles are Equal.
- If each pair of Interior angles on the same side of the transversal are supplementary.

In these cases, the lines have to be in the Parallel condition.
5.5.1 WHAT HAVE WE DISCUSSED?
[embed]https://vimeo.com/455749010/43a8d0b380[/embed]5.5.2 WHAT HAVE WE DISCUSSED? (Notes)
SUMMARY
1. Line has no beginning and no end.
2. Line Segment has a beginning and an end.
3. Ray has a starting point but no ending point.
4. An angle is created with 2 rays having the same starting point.
5. 2 lines are related to each other in :-
Intersecting lines ,
Angles of transversal ,
Transversal of Parallel lines.
6. If the corresponding angles and the pairs of alternate interior angles are equal then the lines are said to be parallel.